What to Know When Adding a Video to Your Website

Adding a video to your website can definitely spruce up the overall design and increase user engagement, but will it affect your site’s load times? Bandwidth costs? Scalability? If you’re unsure about any of these, don’t worry — we’ve got you covered!
Deciding if and how you want to add a video to your website can depend on several key factors. Let’s review them from a development standpoint.
Site Performance
Adding a video to your website can play a significant role in improving the user experience and flow of content. However, one thing to consider is how it will affect your website’s load times and overall performance.
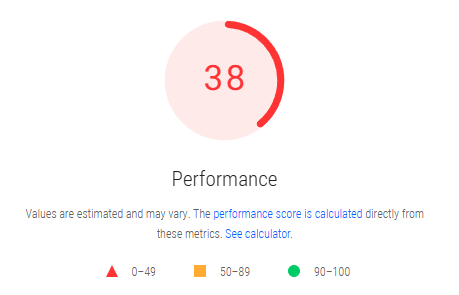
Much like images, videos can be heavy resources for your browser to load onto the web page. Loading a heavy video on your web page not only slows down your site but can also affect your site’s SEO.
Google tends to favor websites that load fast. The faster your website loads, the more likely your rankings are to increase. Let’s take a look at some ways to help your video load faster.
File Size
One of the main components affecting load times is the video’s file size. A user’s internet speed will determine how fast their browser serves the video to the web page; the smaller the video, the faster the video will load. Moreover, a smaller video helps save bandwidth to load other resources.
In any case, shorter videos are always best to reduce the file size. Besides using shorter videos, we suggest using a video compressor on all videos regardless of initial file size. Video compression tools are essential and extremely necessary for reducing file size.
Be cautious when using these tools. The caveat of reducing the file size is lower quality. In general, we can find a happy medium between quality and file size by using shorter videos. The target file size we should aim for is a maximum of 5 MB.
Hosting
We’ve reviewed the importance of reducing file size. Now, let’s review which method is best for serving the video to your website. While this quick guide provides the general basis for hosting options, we still recommend checking your server capabilities and traffic statistics to determine which option is best for your specific website.
Local
Local hosting is typically the quickest solution to implementation. This option is usually for lower-traffic websites or those who need the most control over the video content. Since the video is placed on your own server, you won’t need to worry about third-party branding or privacy issues. That being said, there are still downsides to hosting a video on your own server.
If you plan on using a large video or if your website typically has high traffic, this option might not be for you. Local hosting can increase the load on your server and lead to higher bandwidth usage, which in turn incurs higher hosting costs.
Local hosting can also negatively impact load times and result in buffering issues if your server is not optimized for delivering large media files.
YouTube
Using a video hosting platform like YouTube is another viable option for all ranges of website traffic. By hosting a video on YouTube and loading the video on your website through an iframe, users will be able to view and interact with a UI they are most likely already accustomed to seeing. The setup is pretty simple as well; once a video is uploaded to YouTube, you can share the video on your website through an iframe code that YouTube provides.

Through this option, your local server saves storage space and bandwidth. However, it isn’t a perfect solution on its own. Loading a video from YouTube will automatically call external resources, which can affect your web page’s performance and load time. This is where lazy loading comes in.
Lazy loading is the process of preventing the browser from downloading certain resources until they are needed. For instance, we can use a JavaScript library like Lozad.js to prevent YouTube’s external files from loading onto a webpage until the user interacts with a placeholder element. Pairing lazy loading with YouTube provides a great hosting option if you are looking to have multiple videos on your web page.
Now, let’s take a look at the most well-rounded solution – CDNs.
CDN
A Content Delivery Network, or CDN, is a group of servers that are geographically distributed. When an end user tries to access a resource from a CDN, the server that is closest to them provides the resource from its cache. This enables swift delivery of web content while also reducing local server load. The downside is that this option is typically only recommended for high-traffic websites.
Take a look at your current server utilization. If your server experiences any of these symptoms, then a CDN might be right for you:
- Thousands of concurrent users
- Sudden traffic spikes
- Global audience
- High bandwidth usage
If your website does not receive enough daily traffic, then a CDN might actually hurt more than it may help. For smaller websites with limited budgets, a CDN might not be as cost-effective.
However, if your website fits the above criteria, then switching to a CDN can be a quick way to boost your site’s performance. Here are a few reasons why one of our favorite hosting options is the CDN:
- Using a CDN can significantly improve load times for users, regardless of the geographic location.
- Serving large files like videos with a CDN can free up bandwidth and server load to allow for higher traffic volumes.
- CDNs are often the cheaper solution than upgrading your own server capacity.
- Less stress on your server means less risk of downtime or longer load times
Choosing between different hosting options for your video content depends on your specific needs and resources. Take some time to review your website’s traffic patterns, budget, and server capabilities to make the right choice for hosting your videos.
About Us
Did you know more than 200 clients have worked with PaperStreet for more than 10 years?
Get a Free Website
Analysis and Consultation
Marketing Services